Middleware is a computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as 'software glue'. Middleware makes it easier for software developers to implement communication and input/output, so they can focus on the specific purpose of their application.
- Middleware is the area of specialization dealing with providing environments for developing systems that can be distributed effectively over a myriad of topologies, computing devices and communication networks. It aims to provide developers of networked applications with the necessary platforms and tools to (1) formalize and coordinate.
- Middleware got its name because the first middleware typically acted as a mediator between an application front-end, or client, and a back-end resource - e.g., a database, mainframe application or specialized hardware device - from which the client might request data. But today's middleware operates well beyond this scope.
- Middleware is the key to assembling such an environment. We can think of these capabilities in 4 layers, plus tooling: The container layer. This layer of middleware manages the delivery aspect of application life-cycles in a uniform manner.
Middleware is a type of computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as 'software glue'.[1]
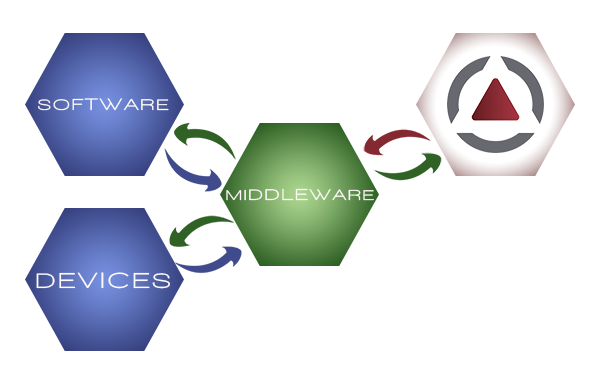
Middleware makes it easier for software developers to implement communication and input/output, so they can focus on the specific purpose of their application. It gained popularity in the 1980s as a solution to the problem of how to link newer applications to older legacy systems, although the term had been in use since 1968.[2]
In distributed applications[edit]
The term is most commonly used for software that enables communication and management of data in distributed applications. An IETF workshop in 2000 defined middleware as 'those services found above the transport (i.e. over TCP/IP) layer set of services but below the application environment' (i.e. below application-level APIs).[3] In this more specific sense middleware can be described as the dash ('-') in client-server, or the -to- in peer-to-peer. Middleware includes web servers, application servers, content management systems, and similar tools that support application development and delivery.[4]
ObjectWeb defines middleware as: 'The software layer that lies between the operating system and applications on each side of a distributed computing system in a network.'[5] Services that can be regarded as middleware include enterprise application integration, data integration, message oriented middleware (MOM), object request brokers (ORBs), and the enterprise service bus (ESB).[6]
Database access services are often characterised as middleware. Some of them are language specific implementations and support heterogeneous features and other related communication features.[7] Examples of database-oriented middleware include ODBC, JDBC and transaction processing monitors.[8]
Distributed computing system middleware can loosely be divided into two categories—those that provide human-time services (such as web request servicing) and those that perform in machine-time. This latter middleware is somewhat standardized through the Service Availability Forum[9] and is commonly used in complex, embedded systems within telecom, defence and aerospace industries.[10]
Other examples[edit]
The term middleware is used in other contexts as well. Middleware is sometimes used in a similar sense to a software driver, an abstraction layer that hides detail about hardware devices or other software from an application.

- The Android operating system uses the Linux kernel at its core, and also provides an application framework that developers incorporate into their applications. In addition, Android provides a middleware layer including libraries that provide services such as data storage, screen display, multimedia, and web browsing. Because the middleware libraries are compiled to machine language, services execute quickly. Middleware libraries also implement device-specific functions, so applications and the application framework need not concern themselves with variations between various Android devices. Android's middleware layer also contains the ARTvirtual machine and its core Java application libraries.[11]
- Middleware also refers to the software that separates two or more APIs and provides services such as rate-limiting, authentication, and logging.
- Game engine software such as Gamebryo and RenderWare are sometimes described as middleware, because they provide many services to simplify game development.[12]
- In simulation technology, middleware is generally used in the context of the high level architecture (HLA) that applies to many distributed simulations. It is a layer of software that lies between the application code and the run-time infrastructure. Middleware generally consists of a library of functions, and enables a number of applications—simulations or federates in HLA terminology—to page these functions from the common library rather than re-create them for each application.[13]
- Wireless networking developers can use middleware to meet the challenges associated with a wireless sensor network (WSN). Implementing a middleware application allows WSN developers to integrate operating systems and hardware with the wide variety of various applications that are currently available.[14]
- The QNX operating system offers middleware for providing multimedia services for use in automobiles, aircraft and other environments.[15]
- Radio-frequency identification (RFID) software toolkits provide middleware to filter noisy and redundant raw data.[16]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
Middleware Definition
- ^'What is Middleware?'. Middleware.org. Defining Technology. 2008. Archived from the original on June 29, 2012. Retrieved 2013-08-11.CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)
- ^Gall, Nick (July 30, 2005). 'Origin of the term middleware'.
- ^'Home'. IETF.
- ^Etzkorn, L. H. (2017). Introduction to Middleware: Web Services, Object Components, and Cloud Computing. CRC Press. pp. 4–5. ISBN9781498754101.
- ^Krakowiak, Sacha. 'What's middleware?'. ObjectWeb.org. Archived from the original on 2005-05-07. Retrieved 2005-05-06.
- ^Luckham, D. C. (2011). Event Processing for Business: Organizing the Real-Time Enterprise. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 27–28. ISBN9781118171851.
- ^Simon, A. R.; Wheeler, T. (2014). Open Client/Server Computing and Middleware. Academic Press. pp. 43–49. ISBN9781483214276.
- ^Arregoces, M.; Portolani, M. (2003). Data Center Fundamentals. Cisco Press. pp. 92–93. ISBN9781587140747.
- ^'Service Availability Interface Specification'(PDF). Service Availability Forum. 30 September 2011. Retrieved 26 July 2018.
- ^Jokiaho, T.; Fryer, J. (2012). 'Foreword'. Service Availability: Principles and Practice. John Wiley & Sons. p. xv. ISBN9781119941675.
- ^Charlie Collins, Michael Galpin and Matthias Kaeppler, Android in Practice, Manning Publications, 2011
- ^Moore, M. E. (2006). Introduction to the Game Industry. Pearson Prentice Hall. p. 169. ISBN9780131687431.
- ^Becchini, R.; Chilaev, P.; Krivtsov, V.; et al. (2003). 'Chapter 4: Middleware'. In Drira, K.; Martelli, A.; Villemur, T. (eds.). Cooperative Environments for Distributed Systems Engineering: The Distributed Systems Environment Report. Springer. pp. 41–4. ISBN9783540455820.
- ^Hadim, S. and Mohamed, N. (2006). Middleware challenges and approaches for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Distributed Systems Online vol 7. Issue 3. Retrieved March 4, 2009 fromiEEE Distributed Systems OnlineArchived 2011-09-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^'QNX Software Joins Internet ITS Consortium of Japan'. QNX News Releases. QNX. 6 May 2008. Retrieved 26 July 2018.
- ^Glover, B.; Bhatt, H. (2006). RFID Essentials. O'Reilly Media. pp. 38–44. ISBN9780596009441.
Middleware Applications
External links[edit]
- The dictionary definition of middleware at Wiktionary

